Is 6000 Engine Hours A Lot? All You Need To Know
When it comes to assessing the longevity and durability of heavy machinery or vehicles, Is 6000 Engine Hours A Lot? This question is crucial for anyone in industries relying on machinery such as construction, agriculture, or transportation. The answer is not straightforward, as it depends on various factors including the type of engine, maintenance history, and the conditions under which the machine operates.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the context of 6000 engine hours.
- Factors influencing the impact of engine hours on machinery.
- Comparing engine hours to human years for better understanding.
- The role of maintenance in prolonging engine life.
Is 6000 Engine Hours A Lot?
Yes, 6000 engine hours can be considered a significant amount for many types of machinery, especially if we compare it to the average lifespan of engines in various industries.

However, this number should not be viewed in isolation. It’s essential to consider the type of engine, its usage, and maintenance history to fully understand its implications.
The Context of 6000 Engine Hours
To put 6000 engine hours into perspective, it’s helpful to compare it to human years. For example, if we consider an average working day for a machine to be similar to that of a human (about 8 hours), then 6000 hours would equate to approximately 750 working days or nearly 3 years of daily use. This comparison helps in understanding the wear and tear that the engine might have undergone.
Factors Affecting Engine Longevity
Several factors contribute to how significantly 6000 engine hours will impact a machine. Key factors include:
- Type of Engine: Diesel engines, for instance, are known for their longevity and can often withstand more hours compared to gasoline engines.
- Maintenance History: Regular maintenance can significantly prolong the life of an engine, even beyond 6000 hours.
- Operating Conditions: Harsh conditions like extreme temperatures or heavy loads can accelerate engine wear.
Maintenance and 6000 Engine Hours
Proper maintenance plays a pivotal role in the lifespan of an engine. Regular servicing, timely replacement of parts, and proper operation can greatly extend the life of an engine beyond the 6000-hour mark.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures that potential issues are addressed before they become major problems. This includes regular oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections.
Impact of Neglect on Engine Hours
Neglecting maintenance can lead to accelerated wear and tear. Even an engine with fewer hours can fail prematurely if not properly maintained.
Comparing Different Engine Types
Different engines respond differently to the accumulation of hours. It’s important to compare and understand how different types of engines fare when they reach the 6000-hour mark.

Diesel vs. Gasoline Engines
Diesel engines are typically more robust and can handle more hours compared to gasoline engines. They are designed for longevity and heavy-duty use.
Heavy Machinery vs. Light Vehicles
Engines in heavy machinery like tractors or excavators are built to endure more stress and longer hours compared to those in light vehicles.
Industry Standards for Engine Hours
Each industry has its own benchmark for what constitutes “a lot” of engine hours. It’s crucial to understand these standards to make informed decisions about machinery.
Construction and Agriculture Industry Standards
In industries like construction and agriculture, engines are expected to last longer due to the heavy-duty nature of the work.
Transportation and Logistics Industry Standards
The transportation industry might have different standards, as the engines are used differently compared to construction or agricultural machinery.
Engine Hours and Resale Value
The number of engine hours significantly impacts the resale value of machinery. Understanding this correlation is essential for both buyers and sellers.
Impact on Buyers
Buyers should be cautious of machinery with high engine hours as it might indicate imminent major repairs or replacements.
Impact on Sellers
Sellers need to be transparent about engine hours to establish trust and ensure a fair transaction.
Evaluating the Impact of Engine Hours on Performance
The impact of engine hours, specifically when reaching the 6000-hour mark, extends beyond just the age of the engine. It significantly influences the performance and efficiency of the machinery. Understanding this impact is crucial for operators to maintain optimal functionality.
Performance Degradation Over Time
As engines accumulate hours, their performance can gradually decline. This decline is not always linear and can be influenced by various factors such as the quality of maintenance and the type of fuel used. For example, components like fuel injectors or turbochargers may become less efficient, resulting in reduced power output and fuel efficiency.
Assessing Performance Through Diagnostics
Regular diagnostic tests are essential to assess the health of an engine. These tests can help identify issues like compression problems or inefficient fuel combustion, which can become more prevalent as engine hours accumulate. Addressing these issues promptly can help maintain performance levels despite high engine hours.
Longevity of Different Engine Models
Not all engines are created equal when it comes to enduring high usage hours. Different models and makes of engines have varying levels of durability and lifespan, which is an important consideration for users.

Engine Design and Durability
The design and build quality of an engine play a significant role in its longevity. Some engines are specifically designed for long-term, heavy-duty use, with components that can withstand prolonged stress better than others.
Manufacturer Reputation and Reliability
The reputation of the manufacturer and the proven reliability of specific engine models are critical factors. Engines from manufacturers known for durability typically can handle more hours without significant performance issues.
The Role of Technology in Engine Longevity
Advancements in technology have a profound impact on the lifespan and efficiency of engines. Modern engines equipped with advanced technologies can often outlast their older counterparts.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technologies like electronic fuel injection, better lubrication systems, and improved cooling systems contribute to the longevity of engines. These advancements allow engines to operate more efficiently, reducing wear and tear over time.
Predictive Maintenance and IoT
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and predictive maintenance algorithms helps in preemptively identifying potential issues before they become major problems. This approach can significantly extend the lifespan of engines, even those with high hour counts.
Environmental Factors and Engine Wear
The environment in which a machine operates plays a significant role in how quickly an engine reaches the 6000-hour mark and how it impacts the engine’s health.

Impact of Harsh Environments
Engines operating in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, dusty or wet environments, or at high altitudes, often experience accelerated wear. These conditions can lead to increased stress on engine components, hastening the onset of performance issues.
Adapting Maintenance to Environmental Conditions
Tailoring maintenance schedules and practices to suit the operating environment can mitigate the adverse effects of harsh conditions. For example, more frequent oil changes or air filter replacements might be necessary in dusty environments to maintain engine health.
Economic Considerations of High Engine Hours
The economic implications of operating machinery with high engine hours are a critical consideration for businesses. It affects operational costs, productivity, and long-term financial planning.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Continued Operation vs. Replacement
Operators must weigh the costs of continued maintenance and potential downtime against the investment in new machinery. In some cases, replacing an engine or machine might be more economically viable than continuing to operate one with high hours.
Impact on Operational Efficiency
Machinery with high engine hours might require more frequent repairs, leading to downtime and reduced operational efficiency. This reduction in efficiency can have a significant impact on the bottom line for businesses relying heavily on machinery.
How Many Engine Hours Is Considered High?
Determining what constitutes “high” engine hours varies significantly depending on the type and usage of the engine. For heavy-duty diesel engines, such as those in trucks and construction equipment, 10,000 to 15,000 hours is often considered high.
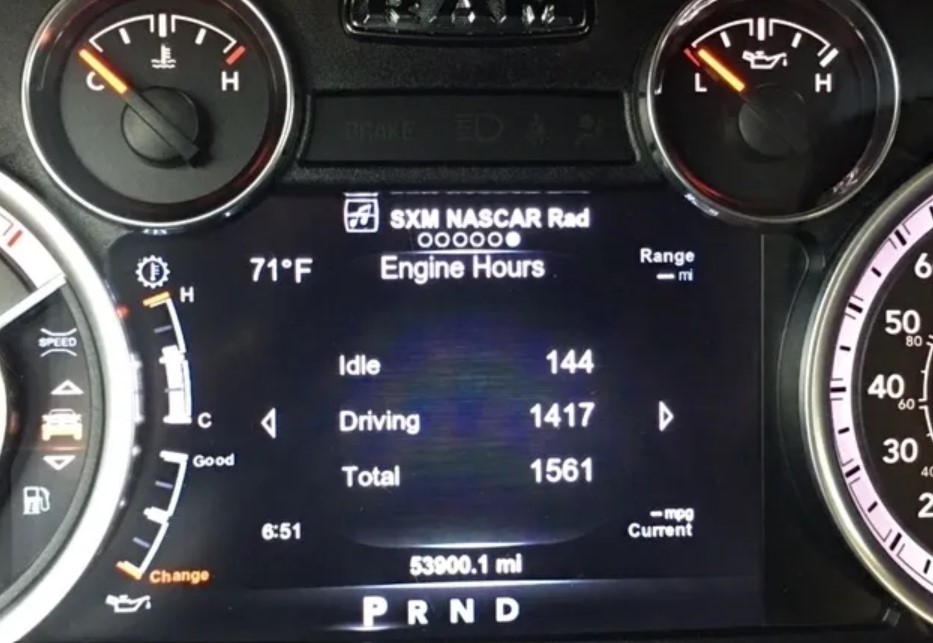
However, for smaller, light-duty gasoline engines, as you might find in smaller vehicles or lawn equipment, 3,000 to 5,000 hours could be deemed high. The key factor is the engine’s design and intended use. Diesel engines, built for durability and long-term use, can handle more hours compared to gasoline engines.
In the marine industry, for example, engines can be considered to have high hours once they reach around 1,500 to 2,000 hours.
This is due to the constant load and often harsh operating conditions. In aviation, turbine engines have a different scale, where several thousand hours might still be mid-life, given the stringent maintenance and operational standards.
It’s essential to consider the context of use: an engine running at full capacity and under stress will accumulate ‘heavier’ hours than one running under light conditions.
Maintenance history also plays a crucial role; well-maintained engines can be considered ‘younger’ in engine hours compared to poorly maintained ones with the same hour count.
How Many Hours Should An Engine Last?
The lifespan of an engine, in terms of hours, depends largely on its type, maintenance, and usage conditions. A well-maintained diesel engine in heavy machinery could last upwards of 20,000 hours before requiring a major overhaul or replacement.
In contrast, a gasoline engine in light-duty equipment might be expected to last between 5,000 to 10,000 hours.
For industrial and agricultural machinery, engines are designed to withstand harsh conditions and heavy usage, leading to longer lifespans. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and timely repairs, significantly extends engine life.
Conversely, engines exposed to severe conditions and poor maintenance might not reach these hour thresholds.
In the marine industry, where engines often operate under constant load, a well-maintained diesel engine can last between 5,000 to 8,000 hours. In aviation, jet engines can operate for tens of thousands of hours with rigorous maintenance and periodic overhauls.
The key to maximizing engine life is adhering to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, using quality parts and fluids, and operating the engine within its design limits.
Technological advancements have also played a role in extending the lifespan of engines, with newer models benefitting from improved materials and engineering.
How Many Miles Is 1 Engine Hour?
The conversion of engine hours to miles is not a straightforward task, as it largely depends on the type of vehicle and its operational conditions. Generally, in the context of trucks or heavy machinery, a rough estimate is that 1 engine hour can be equated to approximately 25 to 30 miles.
This estimation is based on the assumption that the vehicle is operating at a constant speed or under normal working conditions. However, this conversion can vary greatly.

For instance, in vehicles that spend a lot of time idling, such as construction equipment or farm machinery, the miles covered per engine hour could be significantly lower.
It’s important to note that this conversion is an approximation and should be used with caution. The actual distance traveled per engine hour can differ based on factors like driving habits, the nature of the vehicle’s use (e.g., highway driving vs. city driving), and the type of engine.
Are High Engine Hours Bad?
High engine hours are not inherently bad, but they do indicate that an engine has experienced significant use, which can impact its condition and future reliability. The key to understanding the implications of high engine hours lies in considering the engine’s maintenance history and the conditions under which it has operated.
Well-maintained engines with high hours can still be in good condition and offer reliable service.
Regular maintenance, including timely oil changes, filter replacements, and addressing any mechanical issues promptly, can greatly extend the life of an engine, even with high hour counts. On the other hand, an engine with fewer hours but poor maintenance might be in worse condition.
High engine hours can also be a sign of wear and tear on internal components. This wear can lead to decreased efficiency, more frequent repairs, and potentially a shorter remaining lifespan.
Therefore, when considering a vehicle or piece of machinery with high engine hours, a thorough inspection and review of its maintenance records are essential.
How Many Hours Is Too Many On A Semi?
Determining how many hours is “too many” on a semi-truck involves various factors, including the type of engine, maintenance history, and how the truck has been used.
Generally, for modern semi-trucks, engines can last up to 15,000 to 20,000 hours before requiring a major overhaul or replacement, provided they are well-maintained. However, this is a general guideline, and the actual lifespan can vary.

For a semi-truck, the quality and regularity of maintenance are critical. A semi-truck that has been regularly serviced, with oil changes, filter replacements, and timely repairs, can continue to operate effectively even with high engine hours.
Factors such as driving conditions, load weights, and driving habits also play a significant role in the engine’s longevity.
When evaluating a semi-truck, it’s important to look beyond just the engine hours. A comprehensive inspection, review of maintenance records, and understanding of the history of how the truck has been used are essential in determining its condition and remaining lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while 6000 engine hours is a considerable amount, it’s not solely a determinant of an engine’s remaining lifespan or value. Factors like maintenance history, type of engine, and operating conditions play a crucial role. Understanding these aspects can help users make informed decisions about the use, maintenance, and purchase of machinery.
People Also Ask
Can Upgrading Parts Extend the Life of High-Hour Engines?
Upgrading certain parts can enhance performance and potentially extend the life of high-hour engines. This includes installing more efficient cooling systems, better quality filters, or advanced lubrication systems. However, these upgrades should be carefully considered and matched to the engine’s specifications and operating conditions.
How Does the Environment Affect Engine Hours?
Environmental factors like temperature, humidity, dust, and terrain can impact engine wear. Harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or dusty environments, accelerate wear and tear, meaning that engines in these conditions might reach critical wear stages at lower hour counts.
Is It Worth Repairing an Engine with High Hours?
This depends on the engine’s condition and the cost of repairs versus replacement. If the engine is well-maintained and the repairs are manageable, it can be more cost-effective to repair it. However, if the engine requires extensive repairs or is significantly worn, replacement might be a better option.
How Does Engine Load Affect Engine Hours?
Engine load plays a significant role in wear and tear. Engines that consistently operate under high load conditions, like towing heavy loads or working in challenging environments, may experience accelerated wear, making the engine hours more significant in terms of wear and stress.
What Maintenance is Crucial to Extend the Life of an Engine?
Regular maintenance, including oil and filter changes, air filter replacements, and routine inspections of critical components, is essential. Additionally, addressing any issues promptly and using the machinery as per manufacturer guidelines can prolong engine life.

Welcome to the exhilarating world of Matt Rex, a professional car racer turned renowned vehicle enthusiast. Immerse yourself in his captivating blog as he shares heart-pounding adventures, expert reviews, and valuable insights on cars, trucks, jets, and more. Fuel your passion for speed and discover the beauty of vehicles through Matt’s engaging stories and meticulous expertise. Join the ever-growing community of enthusiasts who find inspiration and expert advice in Matt Rex’s blog—a digital hub where the thrill of speed meets the pursuit of knowledge.







