Does Engine Oil Expand When Hot? A Complete Breakdown
Understanding the behavior of engine oil under varying temperatures is crucial for vehicle maintenance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intriguing question: Does Engine Oil Expand When Hot? This topic is not only important for automobile enthusiasts but also for everyday drivers seeking to maintain their vehicles efficiently.
Does Engine Oil Expand When Hot?
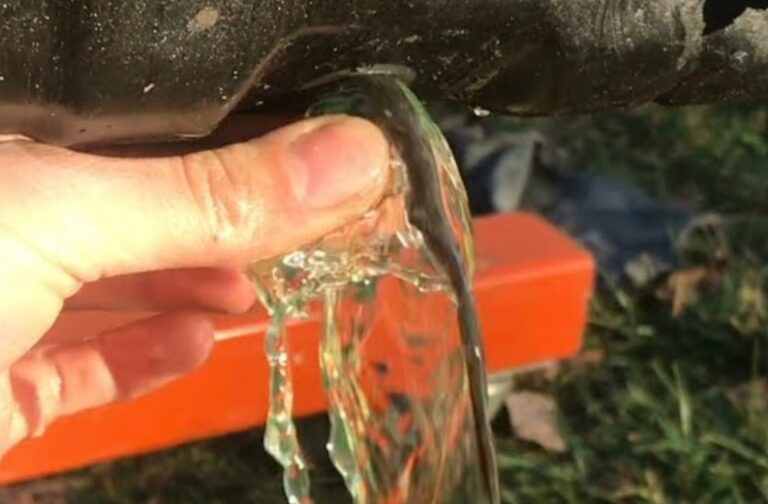
Yes, engine oil does expand when hot. This expansion is a response to the increase in temperature, a fundamental property observed in most liquids. The expansion of engine oil is an essential factor to consider in maintaining optimal engine health.

Why Engine Oil Expands?
- Thermal Expansion: The primary reason for the expansion of engine oil is thermal expansion. As the oil heats up, its molecules move faster and spread apart, leading to an increase in volume.
- Viscosity Changes: Hotter oil tends to be less viscous. This reduced viscosity can make the oil appear to occupy more space, though this is more about flow characteristics than actual volume increase.
Impact on Engine Performance
- Lubrication Efficiency: The expansion can impact lubrication. Thinner, expanded oil may not offer the same protection as thicker, cooler oil.
- Oil Pressure: Increased volume can lead to changes in oil pressure, which is critical for engine health.
Understanding Oil Viscosity
Viscosity, a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow, is a key property of engine oil. It changes with temperature, affecting the oil’s performance.

Viscosity Ratings
- Multi-grade Oils: These oils have additives to ensure they perform well across a range of temperatures.
- Single-grade Oils: More affected by temperature changes, these oils are less commonly used in modern engines.
Choosing the Right Oil
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the right oil viscosity for your vehicle.
- Climate Considerations: In colder climates, oils with a lower viscosity at low temperatures (indicated by the ‘W’ rating) are preferable.
Thermal Expansion of Engine Oil
The degree of expansion varies with oil type and temperature. This section will delve into the specific aspects of how engine oil reacts to heat.
Factors Affecting Expansion
- Oil Composition: Synthetic oils may expand differently compared to conventional oils.
- Temperature Range: The extent of expansion can vary significantly over different temperature ranges.
Measuring Expansion
- Expansion Coefficient: This is a technical measure of how much a specific type of oil expands with temperature changes.
Engine Oil Level and Temperature
Maintaining the correct oil level is critical. Temperature changes can affect how you read the oil level in your vehicle.

Checking Oil Level
- Cold Engine: Checking when the engine is cold might give a more consistent reading.
- Hot Engine: If checking when hot, be aware that the level might appear higher due to expansion.
Importance of Accurate Measurement
- Overfilling Risks: Overfilling can cause frothing and reduced lubrication efficiency.
- Underfilling Risks: Too little oil leads to inadequate lubrication and potential engine damage.
Engine Oil and Temperature Extremes
Engine oil faces challenges not just in hot conditions, but also in extreme cold.
Cold Temperature Effects
- Thickening of Oil: In cold temperatures, oil can thicken, impacting its flow and lubrication properties.
- Startup Wear: Most engine wear happens during startup, particularly in cold weather when oil flow is restricted.
Hot Temperature Effects
- Thinning of Oil: At high temperatures, oil can become too thin, affecting its ability to lubricate effectively.
- Oxidation and Degradation: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to oil breakdown.
Engine Oil Maintenance and Temperature Effects
Proper maintenance of engine oil is critical, especially considering its temperature-dependent behavior. Regular oil changes and monitoring can significantly enhance engine performance and lifespan.
Importance of Regular Oil Changes
- Preventing Oil Breakdown: Over time and with temperature fluctuations, engine oil degrades. Regular changes ensure that your engine is always running on oil with optimal properties.
- Adapting to Seasonal Changes: Changing oil types or viscosities based on the season can help in accommodating temperature-related expansion and viscosity changes.
Monitoring Engine Oil Health
- Oil Analysis: Regular oil analysis can provide insights into the condition of your oil, indicating when a change is necessary.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for color changes or debris in the oil can also indicate the health of your engine oil and by extension, your engine.
Engine Design and Oil Expansion
Modern engines are designed with the knowledge that engine oil expands when hot. This design consideration is crucial in ensuring engine safety and efficiency.

Engine Tolerances and Oil Volume
- Expansion Room: Engines are designed with enough space to accommodate the expansion of oil without causing damage or excessive pressure.
- Oil Channels and Flow: The design of oil channels in an engine takes into account the change in oil viscosity and volume at different temperatures to ensure consistent lubrication.
Advanced Lubrication Systems
- Temperature Regulation: Some high-performance engines include systems to regulate oil temperature, thus maintaining consistent viscosity and volume.
- Oil Pumps and Pressure Relief Valves: These components are designed to adjust to changes in oil volume and pressure, ensuring that the oil flow remains consistent under various temperature conditions.
Environmental and Operational Factors
Various environmental and operational factors can influence the behavior of engine oil, especially its expansion when subjected to high temperatures.
Driving Conditions and Oil Behavior
- Short Trips vs. Long Journeys: Short trips may not heat the oil enough to cause significant expansion, while longer journeys might lead to more noticeable changes.
- Extreme Weather Conditions: In extremely hot or cold climates, the effects on oil expansion and viscosity can be more pronounced, necessitating a more frequent maintenance schedule.
Environmental Impact of Oil Use
- Emissions: Properly maintained oil can help in reducing engine emissions, as it ensures efficient combustion.
- Oil Disposal and Recycling: Responsible disposal and recycling of used engine oil are important for environmental protection, as oil can be harmful if released into the environment.
Advanced Engine Oil Technologies
The development of advanced engine oils is a response to the challenges posed by temperature-related expansion and other factors.

Synthetic Oils and Additives
- Synthetic Oils: These oils are engineered to have more stable properties across a wide temperature range, reducing issues related to expansion.
- Performance Additives: Additives can enhance oil properties, like reducing the rate of degradation at high temperatures and improving lubrication at lower temperatures.
Future Trends in Engine Oil Development
- Eco-Friendly Formulations: There’s a growing trend towards developing more environmentally friendly engine oils.
- Custom Formulations for Electric Vehicles: As the automotive industry evolves, there’s an increasing focus on developing oils suited for electric and hybrid vehicles, where temperature management is still crucial.
Does Engine Oil Rise When Hot?
Engine oil, like most fluids, expands when it is heated. This expansion is due to the increased kinetic energy of the oil molecules, causing them to move further apart.
As the oil’s temperature rises, its volume increases, but its mass remains the same. This phenomenon is known as thermal expansion and is a key consideration in engine design and oil management.
The extent of the expansion depends on the type of oil and the temperature increase. Synthetic oils, for example, may exhibit different expansion characteristics compared to conventional oils.
The design of modern engines takes this expansion into account, providing sufficient space in the oil reservoir to accommodate these changes without causing damage or affecting performance.
Does Oil Get Thicker As It Warms Up?
Contrary to what one might expect, engine oil generally gets thinner, not thicker, as it warms up. Viscosity, which is the measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow, decreases with an increase in temperature.
When engine oil heats up, its viscosity lowers, meaning it flows more easily. This is why warming up your engine is important, especially in colder climates; the oil becomes less viscous and more effective at lubricating the engine.

However, the rate at which oil thins with temperature varies. Multi-grade oils are designed to minimize this effect, maintaining optimal viscosity across a range of temperatures.
The viscosity index (VI) is a measure used to describe how much an oil’s viscosity changes with temperature. Oils with a high VI change less with temperature and are generally preferred for their consistent performance.
How Much Does Engine Oil Expand When Hot?
The extent to which engine oil expands when heated varies based on several factors, including the type of oil and the temperature range. Generally, engine oils can expand by approximately 6% to 10% in volume for every 100 degrees Fahrenheit increase in temperature.
This expansion rate is influenced by the oil’s composition, with synthetic oils typically showing less expansion compared to conventional oils due to their more stable molecular structure.
The expansion coefficient, a specific measure used to describe this change, differs among various oil formulations and is a critical factor considered by engine manufacturers and oil producers.
Effects Of Engine Oil At High Temperature
When engine oil operates at high temperatures, several effects can occur:

- Viscosity Decrease: As previously mentioned, engine oil becomes thinner at high temperatures. This reduction in viscosity can affect the oil’s ability to form a protective lubricating film, potentially leading to increased engine wear.
- Oxidation and Acid Formation: High temperatures can accelerate the oxidation process in engine oil, leading to the formation of acids and sludge. These by-products can corrode engine parts and clog oil passages.
- Evaporation Loss: Engine oil can also experience evaporation loss at high temperatures, leading to a reduction in oil volume and an increase in the concentration of additives and contaminants, which can be detrimental to engine health.
- Thermal Breakdown: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to thermal breakdown of the oil, diminishing its lubricating properties and leading to the formation of deposits inside the engine.
To mitigate these effects, modern engine oils include additives that enhance their high-temperature stability and resistance to oxidation and thermal breakdown.
When To Check Oil Level?
The best time to check the engine oil level is when the engine is cold, or after it has been off for a few hours. This allows the oil to settle in the oil pan, providing a more accurate reading. Checking the oil level when the engine is cold ensures that the oil has not expanded due to heat, which can give a falsely high reading.

For those who need to check the oil level when the engine is warm, it’s recommended to wait at least 10 to 15 minutes after turning off the engine.
This waiting period allows the oil to drain back into the sump and cool down slightly, offering a more reliable reading. It’s important to follow this practice consistently for the most accurate monitoring of oil levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between engine oil and temperature is vital for vehicle maintenance. Engine oil does indeed expand when hot, and this expansion has significant implications for engine performance.
Properly managing oil levels and choosing the right oil viscosity based on your vehicle’s requirements and environmental conditions are critical steps in ensuring your engine’s longevity and efficiency. Remember, regular oil checks and changes are essential in maintaining your vehicle’s health, particularly in light of how temperature affects oil properties.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does engine oil lose its effectiveness faster in hot climates?
Yes, in hot climates, engine oil can degrade faster. High temperatures can accelerate the oxidation process and break down the oil’s additives more quickly. This degradation affects the oil’s viscosity and its ability to lubricate effectively, necessitating more frequent oil changes in hotter environments.
How does cold weather affect engine oil?
In cold weather, engine oil tends to thicken, which can make it flow more slowly. This slow flow can result in inadequate lubrication during engine startup, potentially causing increased engine wear. That’s why it’s crucial to use an oil with an appropriate winter viscosity rating (the ‘W’ in multi-grade oils) in cold climates.
Can overfilling with engine oil damage the engine?
Yes, overfilling your engine with oil can be harmful. It can lead to increased pressure in the crankcase, causing oil to foam and reducing its ability to lubricate effectively. Overfilling can also cause the excess oil to be drawn into the combustion chamber or the crankcase ventilation system, potentially causing damage.
What is the ideal frequency for checking engine oil levels?
It’s generally recommended to check your engine oil level at least once a month and before any long trip. Consistent monitoring helps in maintaining the correct oil level, considering that oil can expand when hot and contract when cold.
Is synthetic oil better for high-temperature operation?
Synthetic oils are generally better for high-temperature operation. They are designed to have a more stable viscosity across a broad temperature range and resist breakdown at higher temperatures better than conventional oils.

Welcome to the exhilarating world of Matt Rex, a professional car racer turned renowned vehicle enthusiast. Immerse yourself in his captivating blog as he shares heart-pounding adventures, expert reviews, and valuable insights on cars, trucks, jets, and more. Fuel your passion for speed and discover the beauty of vehicles through Matt’s engaging stories and meticulous expertise. Join the ever-growing community of enthusiasts who find inspiration and expert advice in Matt Rex’s blog—a digital hub where the thrill of speed meets the pursuit of knowledge.