Can You Use #2 Fuel Oil In A Diesel Engine? [Answered]
This article will explain Can You Use #2 Fuel Oil In A Diesel Engine? Exploring the use of #2 Fuel Oil in Diesel Engines reveals a complex yet fascinating intersection of chemistry, engineering, and practicality. This topic, often overlooked, delves into the heart of modern engine technology and fuel efficiency.
Understanding the compatibility and implications of using #2 fuel oil in diesel engines is not just about knowing if it’s possible; it’s about appreciating the nuances of engine performance and longevity.
Key Takeaways
- #2 Fuel Oil can be used in diesel engines but with considerations regarding engine design and fuel quality.
- The energy content and viscosity of #2 fuel oil are critical factors influencing its use in diesel engines.
- Long-term use of #2 fuel oil in diesel engines might lead to maintenance and operational issues.
- Environmental impacts and legal regulations play a role in the decision to use #2 fuel oil in diesel engines.
Can You Use #2 Fuel Oil In A Diesel Engine?
Yes, #2 Fuel Oil can be used in diesel engines, but it’s crucial to understand the intricacies of this choice. #2 Fuel oil, commonly known as home heating oil, has properties similar to diesel.

However, differences in sulfur content, viscosity, and cetane numbers mean that its use in diesel engines requires careful consideration.
Understanding #2 Fuel Oil
#2 Fuel oil is a middle distillate, much like diesel, and is primarily used for heating. Its characteristics, such as low viscosity and high energy content, make it a candidate for use in diesel engines. However, the nuances in its composition compared to standard diesel fuel can lead to varying engine performance and maintenance requirements.
Comparing #2 Fuel Oil and Diesel
The primary differences between #2 fuel oil and standard diesel lie in their sulfur content and cetane number. While diesel fuel is formulated specifically for engine performance, #2 fuel oil is optimized for heat output, posing potential challenges when used in diesel engines.
Engine Compatibility and Performance
Using #2 fuel oil in a diesel engine hinges heavily on the engine’s design and tolerance. Modern diesel engines, especially those with high precision fuel injectors and tight emission controls, may not be as compatible with #2 fuel oil compared to older, less sophisticated models.
Modern Diesel Engines
Newer diesel engines are designed with stringent emission standards in mind. The use of #2 fuel oil in these engines could lead to increased wear and tear, inefficiencies, and potential violations of emission regulations.
Older Diesel Engine Considerations
In contrast, older diesel engines, with their less complex designs and more robust nature, might accommodate #2 fuel oil more readily. However, even in these engines, the use of #2 fuel oil over long periods can lead to increased maintenance and potential performance issues.
Maintenance and Operational Aspects
The use of #2 fuel oil in diesel engines can influence maintenance schedules and operational reliability. The fuel’s properties, differing from standard diesel, can lead to increased deposit formation, wear on fuel system components, and challenges in cold weather operation.
Impact on Maintenance
Regular use of #2 fuel oil in diesel engines might necessitate more frequent maintenance routines. Fuel filters, injectors, and other components may require closer attention due to the different combustion characteristics of #2 fuel oil.
Operational Considerations
Operational aspects, such as cold weather performance and fuel stability, are also impacted when using #2 fuel oil in diesel engines. The fuel’s behavior in low temperatures and its long-term stability can pose challenges for reliable engine operation.
Environmental and Regulatory Factors
The decision to use #2 fuel oil in a diesel engine is not purely a technical one. Environmental considerations and legal regulations play a significant role. The sulfur content and emissions profile of #2 fuel oil can be at odds with modern environmental standards, making its use in diesel engines a matter of regulatory compliance as well as environmental responsibility.
Environmental Impacts
Using #2 fuel oil in diesel engines could lead to higher emissions, contributing to environmental concerns. The sulfur content, in particular, is a significant factor, as it can lead to increased particulate emissions.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Regulations regarding fuel use in diesel engines are stringent and vary by region. The use of #2 fuel oil might not comply with these regulations, especially in areas with strict emission standards. It’s essential to be aware of and adhere to local laws when considering the use of alternative fuels in diesel engines.
Is Number 2 Fuel Oil The Same As Diesel?
Number 2 fuel oil and diesel are often considered similar, but they are not exactly the same. Both fuels are derived from petroleum and belong to the category of middle distillates.
The primary differences lie in their intended use, formulation, and regulatory standards. Number 2 fuel oil, commonly used for heating, has a higher sulfur content compared to on-road diesel.
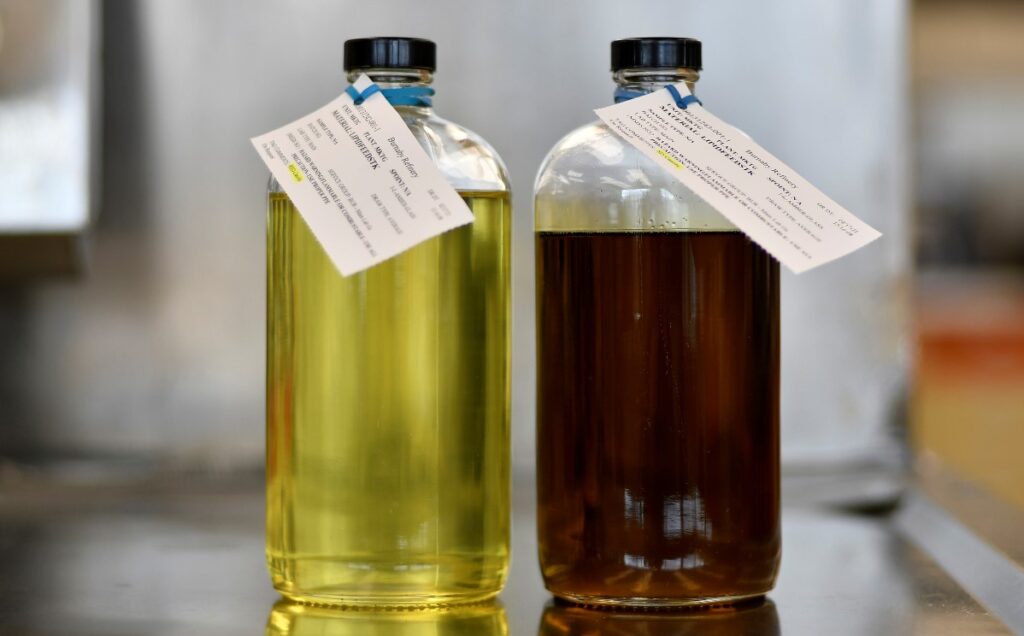

This difference in sulfur content significantly affects the fuel’s environmental impact and combustion characteristics. Diesel, on the other hand, is specifically formulated for use in diesel engines, with additives that enhance engine performance and reduce emissions.
While they share some similarities in composition and energy content, the specific additives and refinement processes for diesel are tailored to meet the needs of modern diesel engines and stringent emission regulations. These differences are critical when considering the use of one as a substitute for the other.
Can I Use Fuel Oil In A Diesel Engine?
Using fuel oil in a diesel engine is technically possible, but it comes with several caveats. Fuel oil, particularly Number 2 fuel oil, shares some characteristics with diesel fuel, such as energy content and density.
However, the differences in sulfur content, viscosity, and cetane rating between fuel oil and diesel can lead to issues in engine performance, emissions, and maintenance.
Modern diesel engines, which are designed to meet strict emission standards and use low-sulfur diesel fuels, may suffer from increased wear and tear, deposit formation, and efficiency losses when operated with fuel oil.
Additionally, the legal and environmental implications of using high-sulfur fuel oil in a diesel engine, particularly in regions with stringent emission laws, must be considered.
Can You Put Diesel #2 In A Diesel Truck?
Yes, you can put Diesel #2 in a diesel truck. Diesel #2 is essentially the standard diesel fuel used for most diesel-powered vehicles, including trucks, in colder climates. It has a lower gel point compared to Diesel #1, making it suitable for use in colder temperatures.

Diesel #2 provides the necessary lubrication and energy content required for diesel engines and is formulated to ensure proper engine performance and longevity. The use of Diesel #2 in diesel trucks is standard practice, and this fuel meets the requirements set by engine manufacturers and emission regulations.
Can You Use Diesel In Place Of Number 2 Oil In A Furnace?
Using diesel in place of Number 2 oil in a furnace is possible as both fuels are similar in terms of energy content and combustion properties. In emergency situations or when heating oil is not available, diesel can serve as a substitute to keep a furnace operational.
However, it’s important to note that diesel is typically more expensive than heating oil due to different taxation and distribution costs.
Additionally, while diesel can be a suitable temporary substitute, long-term use in a furnace designed for heating oil may not be ideal due to differences in fuel composition and the potential for increased maintenance requirements.
Can Heating Oil Be Used As A Diesel Substitute In A Diesel Engine?
Heating oil, particularly Number 2 heating oil, can be used as a substitute in a diesel engine, but with several important considerations. The key differences between heating oil and diesel, such as sulfur content and additive packages, can impact engine performance and emissions.

In older diesel engines, which are less sensitive to fuel variations, heating oil might be used with fewer issues. However, in modern diesel engines, especially those with advanced emission control systems, using heating oil can lead to increased engine wear, reduced efficiency, and potential violations of emission standards.
Furthermore, the legal implications of using heating oil in a diesel engine, especially on-road vehicles, should be considered, as it may not comply with fuel taxation and environmental regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while #2 fuel oil can technically be used in diesel engines, this choice comes with a series of significant considerations.
Engine compatibility, maintenance requirements, operational challenges, environmental impacts, and regulatory compliance all play crucial roles in determining the feasibility and advisability of using #2 fuel oil in diesel engines.
Balancing these factors is key to making an informed decision that ensures both engine performance and adherence to environmental standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I consider before using #2 fuel oil in my diesel engine?
Consider engine compatibility, maintenance implications, environmental and legal aspects, and potential impacts on performance and longevity. It’s also advisable to consult with a professional or the engine manufacturer before making such a switch.
Can I mix #2 fuel oil with diesel in my engine?
Mixing fuels is generally not recommended unless specified by the engine manufacturer. Mixing #2 fuel oil with diesel can lead to unpredictable engine performance and potential damage.
Does #2 fuel oil offer better performance in diesel engines?
Not necessarily. While #2 fuel oil has a similar energy content to diesel, its different chemical properties can lead to suboptimal combustion and performance issues in engines designed specifically for diesel.
Is #2 fuel oil more cost-effective than diesel for engine use?
While #2 fuel oil might be cheaper in some regions, the potential increased maintenance costs and risk of engine damage can offset the initial savings. Additionally, the cost-effectiveness can vary based on local fuel prices and availability.

Welcome to the exhilarating world of Matt Rex, a professional car racer turned renowned vehicle enthusiast. Immerse yourself in his captivating blog as he shares heart-pounding adventures, expert reviews, and valuable insights on cars, trucks, jets, and more. Fuel your passion for speed and discover the beauty of vehicles through Matt’s engaging stories and meticulous expertise. Join the ever-growing community of enthusiasts who find inspiration and expert advice in Matt Rex’s blog—a digital hub where the thrill of speed meets the pursuit of knowledge.







