Can You Bend Valves By Turning Engine By Hand? Answered
Understanding the mechanics of an engine is crucial for any automotive enthusiast or professional. A common query that often arises is, Can You Bend Valves By Turning Engine By Hand? This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of this topic, delving into the intricacies of engine operation and the impact of manual rotation on engine valves.
Key Takeaways
- Manual engine rotation typically does not cause valve bending.
- Valve bending is more likely due to timing issues or mechanical failure.
- Regular maintenance and proper techniques are essential to prevent damage.
Can You Bend Valves By Turning Engine By Hand?
Turning an engine by hand is unlikely to bend valves. Valve bending typically occurs due to timing belt or chain failure, not manual rotation. However, certain conditions must be considered to avoid any potential damage.
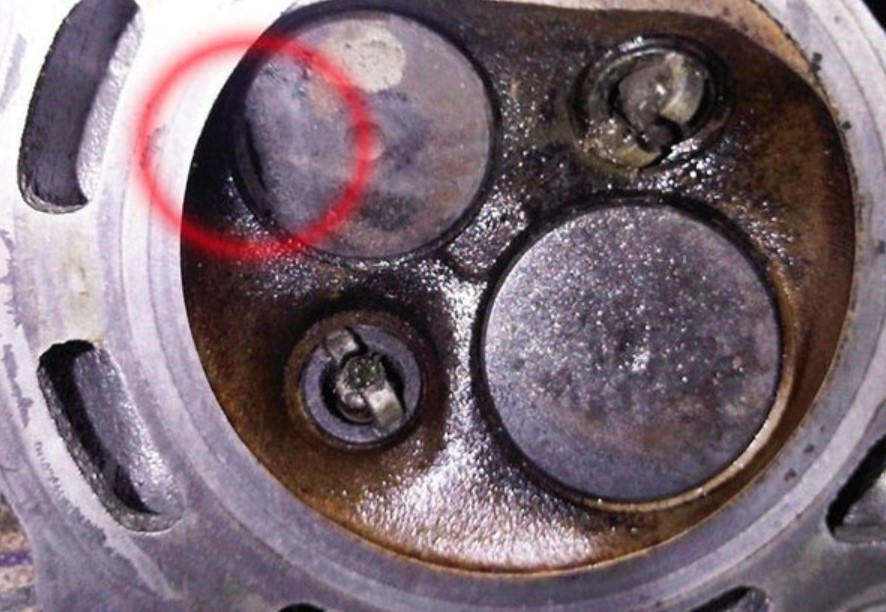

Factors Influencing Valve Safety
When turning an engine manually, it’s crucial to understand the position of the pistons and the state of the engine’s timing components.
Best Practices for Manual Engine Rotation
Adhering to specific techniques can ensure safe and damage-free manual rotation of the engine.
The Mechanics of Engine Operation
Engines are complex machines with numerous moving parts. The interplay between these parts determines the engine’s efficiency and functionality.
Understanding Valve Operation
Valves play a crucial role in an engine’s operation. They control the flow of air and fuel into the engine and the exit of exhaust gases. Proper valve timing is key to efficient engine performance.
The Risk of Valve Damage
Turning an engine by hand is a common practice during maintenance or troubleshooting. However, there’s a general concern about the potential risk of bending valves during this process.
Common Misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding the manual rotation of engines and valve safety.
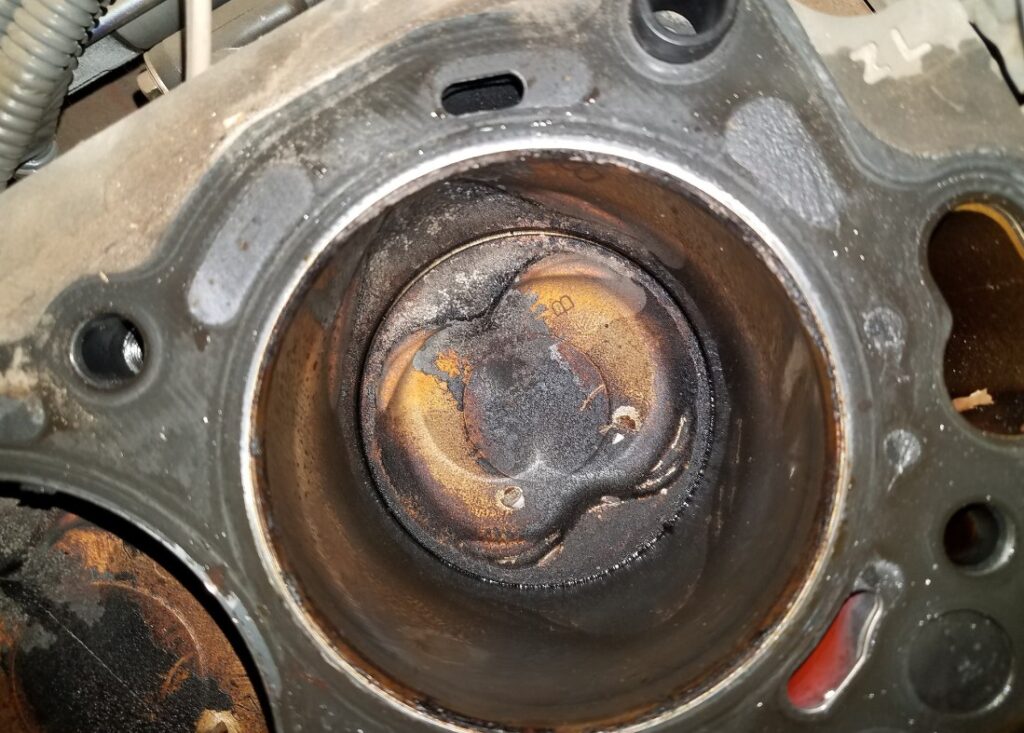

Separating Fact from Fiction
Understanding the reality behind these misconceptions is crucial for proper engine maintenance and handling.
Impact of Myths on Engine Maintenance
Misinformation can lead to unnecessary caution or improper handling, potentially causing more harm than good.
Preventive Measures and Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance and the right techniques are key to preventing valve damage during engine handling.
Importance of Regular Engine Checks
Routine inspections and timely replacement of critical components like timing belts can avert potential valve damage.
Tips for Safe Manual Engine Handling
Adopting certain practices and precautions ensures that manual engine handling does not lead to valve bending.
Advanced Considerations
An in-depth understanding of engine mechanics and handling can further mitigate the risk of valve damage.
Technical Insights
Delving deeper into engine dynamics and valve operation offers a more nuanced perspective on the subject.
Case Studies and Real-World Scenarios
Analyzing real-life instances where manual engine rotation led to issues provides practical insights and learning opportunities.
Can You Bend Valves By Cranking Engine?
Bending valves by simply cranking an engine is unlikely under normal conditions. Valves typically bend due to timing issues – like a timing belt or chain failure – where the synchronized movement of pistons and valves is disrupted.
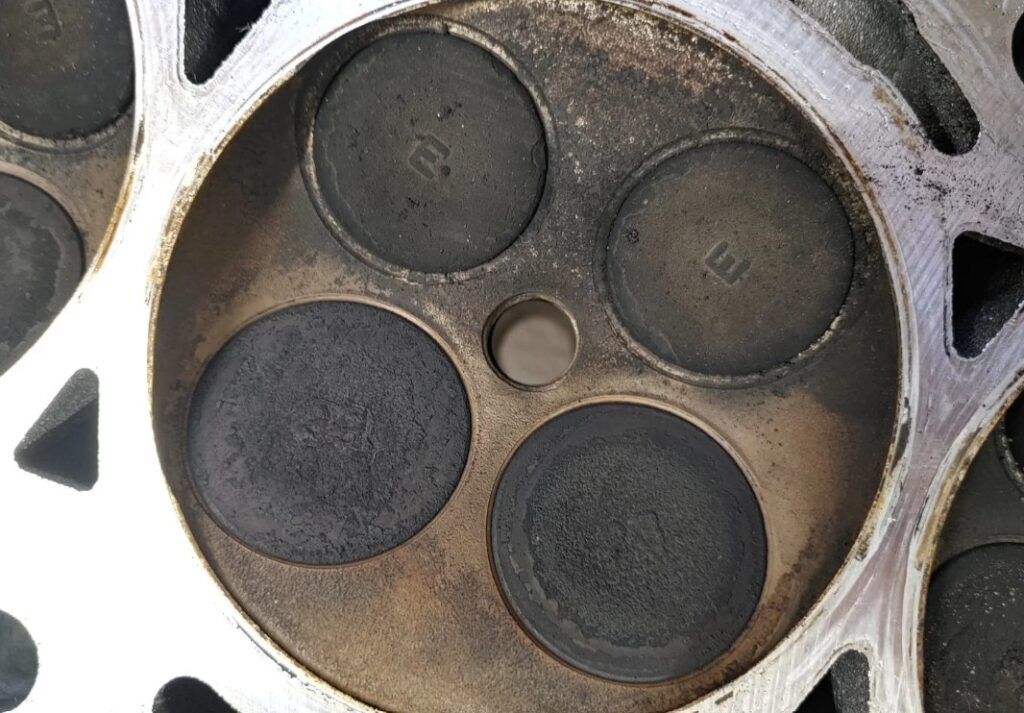

When the timing components fail, especially in interference engines where the piston and valve paths intersect, the piston may strike an open valve during its cycle, leading to bending.
Cranking an engine, in the absence of such timing mishaps, does not exert the kind of force needed to bend valves. It’s essential to ensure that timing components are in good condition and properly synchronized to prevent such issues.
What Are The Symptoms Of Bent Valves In Engine?
The symptoms of bent valves in an engine are often quite noticeable. These include:
- Poor Engine Performance: The engine may run unevenly or misfire, resulting from improper sealing of the combustion chamber.
- Strange Noises: Tapping or knocking sounds from the engine can indicate valve damage.
- Loss of Power: Bent valves can lead to a loss of engine power or a noticeable decrease in performance.
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle roughly or stall due to the disruption in the air-fuel mixture and exhaust flow.
- Compression Loss: A compression test may reveal lower compression in one or more cylinders, indicating valve issues.
These symptoms arise because bent valves fail to close properly, leading to air leaks and inefficiencies in the combustion process.
How Do You Check For Bent Valves Without Removing Head?
Checking for bent valves without removing the cylinder head involves a few indirect methods:
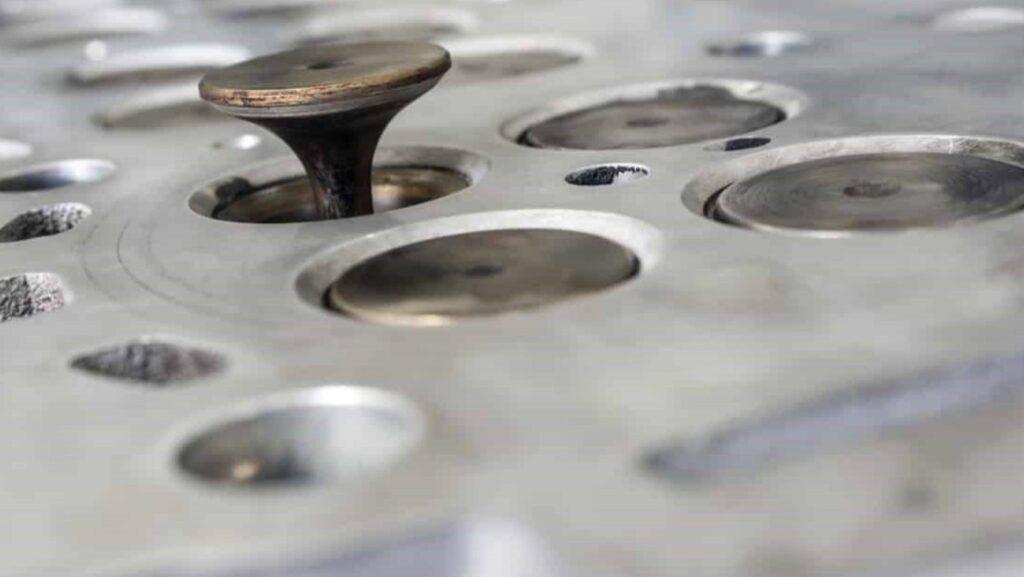

- Compression Test: A compression test can indicate a loss of compression in affected cylinders, which may suggest valve issues.
- Leak-Down Test: This test involves introducing air into the cylinder at top dead center and measuring the rate at which it escapes. If there’s significant leakage, bent valves could be a cause.
- Vacuum Test: A vacuum gauge can help diagnose bent valves. Fluctuating vacuum readings often point to valve train problems, including bent valves.
- Listening to Engine Sounds: Sometimes, abnormal engine sounds can suggest valve issues. Using a stethoscope, mechanics can listen for any irregular tapping or clicking noises from the valve area.
While these methods can provide indications, they cannot definitively confirm bent valves without physical inspection.
Can You Start A Car With Bent Valves?
Starting a car with bent valves is possible, but it is not advisable. Bent valves can cause serious engine issues, including:
- Poor Engine Operation: The engine may start but run poorly, with misfires, rough idling, or stalling.
- Potential for Further Damage: Running an engine with bent valves can lead to more severe damage, such as damaging the piston, cylinder head, or other valve train components.
- Reduced Engine Lifespan: Operating a vehicle with bent valves can significantly shorten the engine’s lifespan.
Therefore, if bent valves are suspected, it is recommended to address the issue before attempting to start and run the engine to avoid further damage.
Conclusion
In summary, while turning an engine by hand is generally safe and unlikely to cause valve bending, it’s imperative to approach this task with knowledge and caution.
Regular maintenance, understanding of engine mechanics, and adherence to best practices are key to ensuring the health and longevity of your engine. Remember, informed handling is the best defense against potential engine damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs of valve damage after manually rotating an engine?
Signs of valve damage might include unusual noises during engine operation, misfiring, loss of engine power, or even compression loss in severe cases. If any of these symptoms are noticed after manually rotating an engine, a thorough inspection by a professional is recommended.
How often should you manually rotate an engine as part of maintenance?
Regularly rotating an engine is not typically part of standard maintenance. However, it can be beneficial in certain situations, like when a vehicle has been stationary for an extended period, to ensure that internal components are not seizing up.
What are the risks of turning an engine backwards?
Turning an engine in the opposite direction of normal operation can potentially cause timing issues, especially in engines with timing belts. It can lead to belt slippage or jumping, which can result in improper timing and potential valve damage.
Can rotating an engine manually help in diagnosing engine issues?
Yes, manually rotating the engine can help diagnose issues such as seized components, abnormal mechanical resistance, or timing problems. It allows for a controlled inspection of the crankshaft, pistons, and valves’ movement.

Welcome to the exhilarating world of Matt Rex, a professional car racer turned renowned vehicle enthusiast. Immerse yourself in his captivating blog as he shares heart-pounding adventures, expert reviews, and valuable insights on cars, trucks, jets, and more. Fuel your passion for speed and discover the beauty of vehicles through Matt’s engaging stories and meticulous expertise. Join the ever-growing community of enthusiasts who find inspiration and expert advice in Matt Rex’s blog—a digital hub where the thrill of speed meets the pursuit of knowledge.






![Allison MT643 Transmission Problems [Fixed]](https://www.turbochaos.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Allison-MT643-Transmission-Problems-768x547.jpg)