How To Turbocharge A Carbureted Engine? 10 Working Steps
Turbocharging a carbureted engine is an art. It’s about understanding the harmony between a classic fuel system and advanced forced induction technology. This process demands precision and knowledge, ensuring the old-school engine breathes new life with added power and efficiency. Let’s explore How To Turbocharge A Carbureted Engine? maintaining its essence while significantly boosting performance.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the Basics: Comprehend the fundamentals of turbocharging and carbureted engines.
- Selecting the Right Turbocharger: Choose a turbocharger that suits your engine’s specifications and needs.
- Carburetor Modifications: Learn about necessary changes to the carburetor for optimal performance.
- Installation Process: Step-by-step guide on installing a turbocharger on a carbureted engine.
- Tuning for Performance: Fine-tune your engine for reliability and maximum power.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular checks and maintenance tips to ensure longevity.
How To Turbocharge A Carbureted Engine?
Turbocharging a carbureted engine is a complex process that involves several critical steps. Each step requires precision and careful consideration to ensure the engine not only gains increased power but also maintains reliability. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
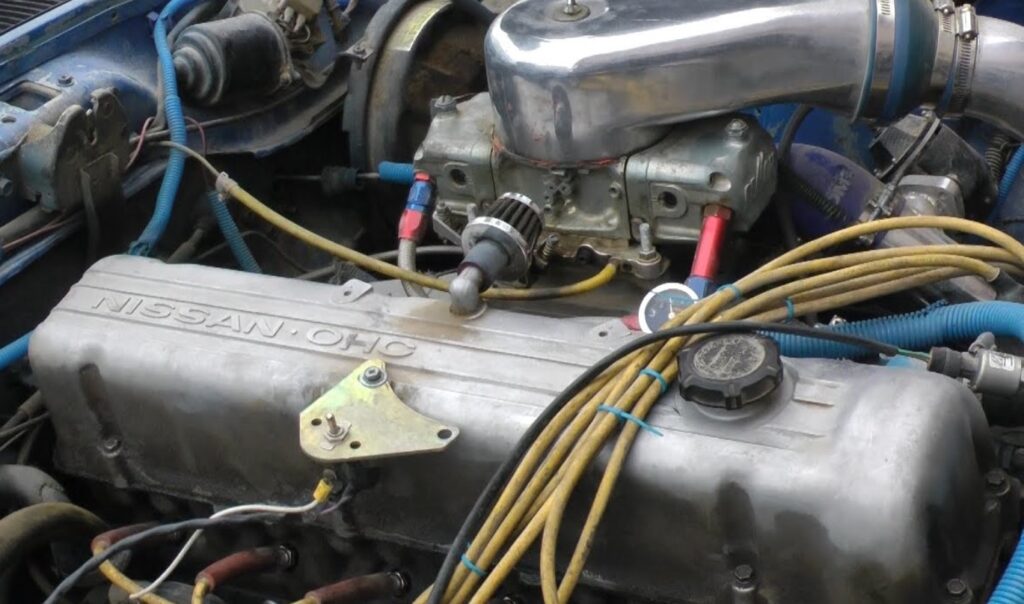

- Selecting the Right Turbocharger:
- Compatibility: Choose a turbocharger that is compatible with your engine’s displacement and power goals. Consider factors like engine size, the desired amount of boost, and the type of driving you plan to do.
- Sizing: The size of the turbocharger is crucial. A turbo that’s too large can lead to lag, while a small one might not provide the desired boost. Balance is key for optimal performance.
- Modifying the Carburetor:
- Upgrading for Pressure: Standard carburetors aren’t built for the pressure that a turbocharger introduces. You might need a special blow-through carburetor or modifications to your existing one.
- Adjusting Fuel Jets and Float Bowl: Adjust the fuel jets for richer fuel delivery and modify the float bowl to prevent fuel starvation under boost.
- Installing the Turbocharger:
- Exhaust Manifold: Replace or modify the exhaust manifold to accommodate the turbocharger.
- Mounting the Turbocharger: Carefully mount the turbocharger, ensuring it’s securely attached and aligned with the exhaust and intake systems.
- Oil Lines: Turbochargers need a good oil supply for lubrication and cooling. Install oil feed and return lines from the engine to the turbo.
- Intercooler Installation (Optional but Recommended):
- Reducing Air Temperature: An intercooler cools the air compressed by the turbo, increasing its density and improving combustion in the engine.
- Placement: It should be placed where it can receive good airflow, typically at the front of the vehicle.
- Modifying the Exhaust System:
- Downpipe: Install a downpipe that leads from the turbocharger’s exhaust outlet to the rest of the exhaust system.
- Exhaust Flow: Ensure the exhaust system is free-flowing to maximize the turbo’s efficiency.
- Integrating the Turbo with the Carburetor:
- Piping: Connect the turbocharger to the carburetor using appropriate piping. This can be complex in a draw-through setup.
- Air/Fuel Mixture: Ensure the carburetor is delivering the correct air-fuel mixture for boosted conditions.
- Tuning the Engine:
- Air-Fuel Ratio: Adjust the carburetor for the correct air-fuel ratio, crucial for preventing engine knock and ensuring efficient performance.
- Ignition Timing: Retard the ignition timing to prevent pre-ignition and detonation, which are common problems when introducing forced induction.
- Boost Pressure: Set up a boost controller to manage the turbocharger’s boost level, balancing power output with engine safety.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Regular Checks: Regularly inspect the turbocharger, carburetor, and related components for signs of wear or leaks.
- Oil Changes: Frequent oil changes are essential, as turbochargers can put extra strain on the engine oil.
- Testing and Adjustments:
- Initial Testing: Start the engine and let it idle to check for any immediate issues.
- Road Testing: Carefully test the car under different conditions to check the turbocharger’s performance and make any necessary adjustments.
- Safety and Legal Considerations:
- Safety Measures: Ensure all components are installed securely to handle the increased power and speed.
- Legal Compliance: Check local laws and regulations regarding modifications to ensure your vehicle remains street-legal.
Understanding the Basics
Before turbocharging your engine, it’s crucial to understand both the turbocharger’s role and the carburetor’s function. A turbocharger compresses air into the engine, allowing more fuel to burn and thus increasing power. Carburetors, on the other hand, are responsible for mixing air and fuel in older engine models. The synergy between these two components is vital for a successful upgrade.
The Role of a Turbocharger
A turbocharger consists of a turbine and a compressor. Exhaust gases drive the turbine, which in turn powers the compressor to force more air into the engine. This process significantly increases the air density inside the engine, allowing for a more efficient fuel burn and higher power output.
The function of a Carburetor
The carburetor is an older fuel-mixing technology, replaced largely by fuel injection in modern engines. It mixes air and fuel in the right proportion before feeding it into the engine. When adding a turbocharger, modifications to the carburetor are necessary to handle the increased air pressure and volume.
Selecting the Right Turbocharger
Choosing the appropriate turbocharger for your carbureted engine is a critical step. It involves understanding your engine’s capacity, the desired power output, and compatibility with the carburetor.
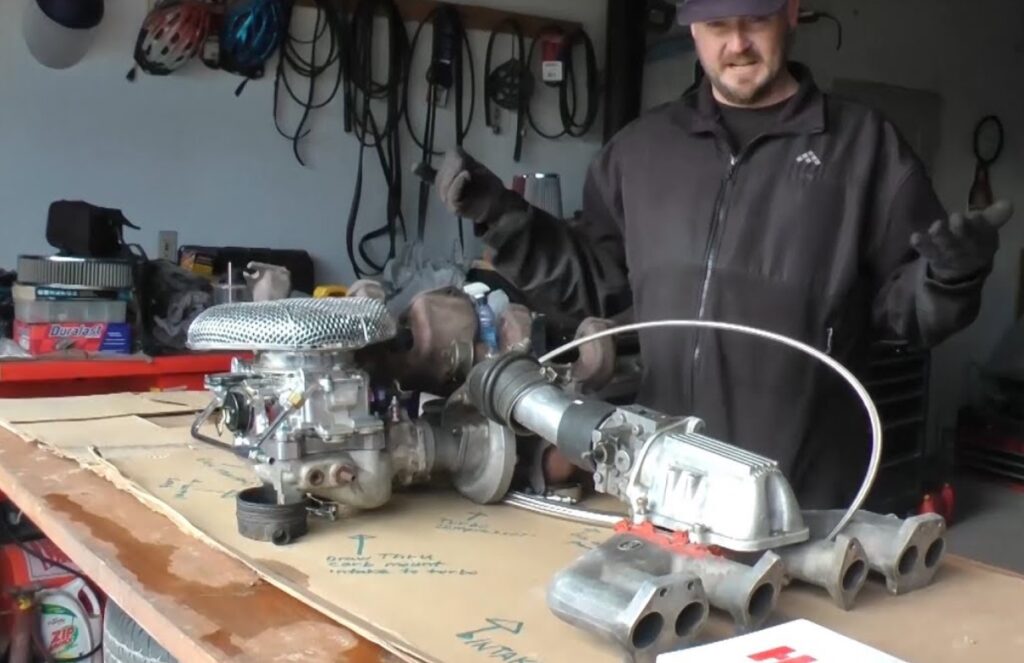

Matching Turbocharger to Engine Size
It’s essential to select a turbocharger that matches your engine’s displacement and power goals. A turbo too large can lead to lag, while one too small won’t provide the desired boost.
Compatibility with Carbureted Systems
Not all turbochargers are suitable for carbureted engines. Special considerations, like the carburetor’s ability to handle pressurized air, are key factors in your selection process.
Carburetor Modifications
To integrate a turbocharger with a carbureted engine, certain alterations to the carburetor are required. These modifications ensure that the carburetor can handle the increased air pressure and volume brought by the turbocharger.
Adjusting for Boosted Air Pressure
The carburetor must be modified to operate under the higher air pressure conditions created by the turbocharger. This often involves reinforcing certain components and adjusting the fuel delivery system.
Ensuring Proper Fuel Mixture
With increased air density from the turbocharger, the carburetor must be adjusted to provide the correct fuel mixture for optimal combustion. This is crucial for preventing engine knock and ensuring efficient performance.
Installation Process
Installing a turbocharger on a carbureted engine involves several steps, each requiring precision and attention to detail.
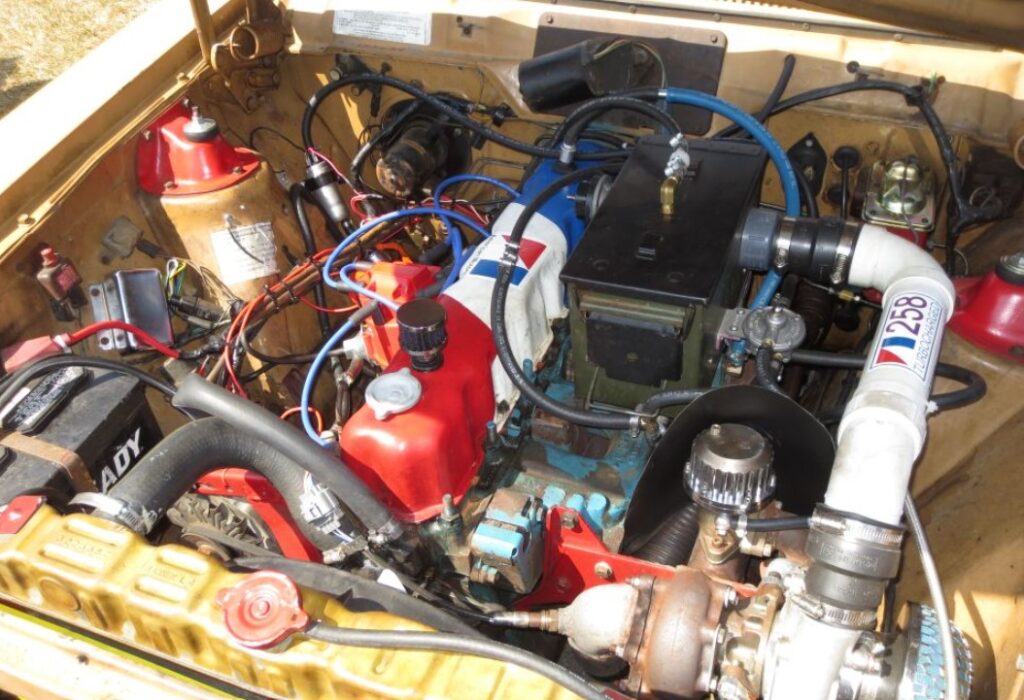

Preparing the Engine
Before installing the turbocharger, it’s important to prepare your engine. This includes ensuring all components are in good condition and capable of handling the increased power.
Turbocharger Installation Steps
- Mount the Turbocharger: Securely attach the turbocharger to the engine, ensuring proper alignment with the exhaust and intake systems.
- Connect the Oil Lines: Turbochargers require a steady oil supply. Install and connect oil lines for proper lubrication.
- Integrate with the Carburetor: Connect the turbocharger to the modified carburetor, ensuring airtight seals.
Tuning for Performance
Once installed, tuning the turbocharged carbureted engine is crucial for optimal performance.
Balancing Air-Fuel Mixture
Adjust the carburetor to provide the right air-fuel mixture, ensuring the engine runs smoothly and efficiently under boosted conditions.
Setting the Boost Level
Determine the appropriate boost level for your engine. This involves balancing power output with engine reliability and longevity.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for the longevity of your turbocharged carbureted engine.
Routine Checks
Regularly check the turbocharger and carburetor for signs of wear or damage. Pay special attention to oil lines and seals.
Scheduled Maintenance
Perform scheduled maintenance on your turbocharged engine, focusing on the unique demands of the added turbocharger and the carbureted fuel system.
How To Turbo A Carbureted Car?
Turbocharging a carbureted car involves several key steps. First, select a turbocharger that matches your engine’s specifications. Then, modify the carburetor to handle the increased air pressure, ensuring it can still mix the fuel and air correctly under boosted conditions.
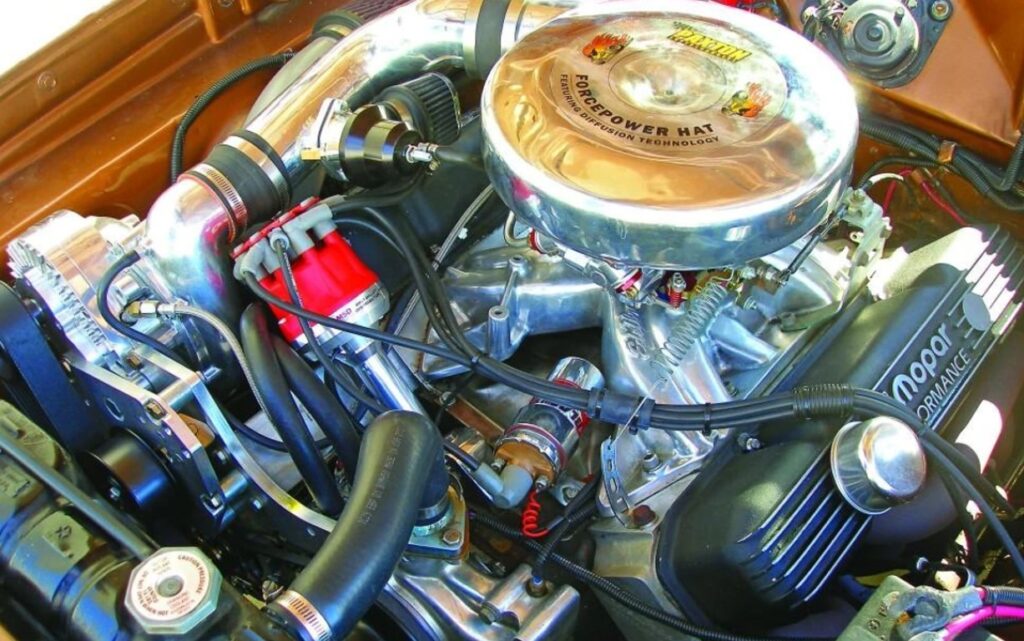

The fuel delivery system may need upgrading to supply more fuel. Install the turbocharger, connect it to the exhaust and intake systems, and modify or replace the exhaust manifold to accommodate the turbo.
Finally, tune the engine for the correct air-fuel mixture and desired boost levels. Professional assistance is highly recommended for both installation and tuning.
Why Is This Difficult To Do?
Turbocharging a carbureted car is challenging due to the nature of carburetors and the complexity of turbo systems. Carburetors, designed for naturally aspirated engines, struggle with the fluctuating pressures and the richer fuel mixtures required for turbocharged applications.
Additionally, the process involves precise tuning to balance the air-fuel mixture and boost levels, which can be intricate and requires a deep understanding of both the carburetor and turbocharger functions. The need for additional upgrades, like stronger internal engine components and improved fuel delivery systems, adds to the complexity.
Can You Turbo Charge A Carbureted Engine?
Yes, you can turbocharge a carbureted engine, but it requires significant modifications. The carburetor must be adapted to manage the increased air pressure and volume from the turbocharger.
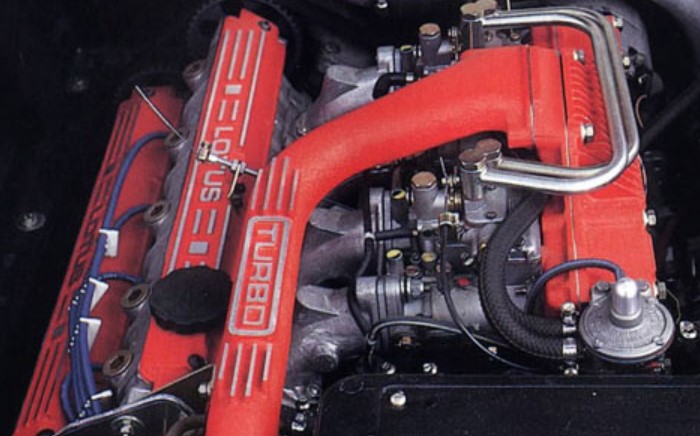
Often, this involves using a blow-through carburetor setup, where the carburetor is placed after the turbo in the airflow path, or a draw-through setup, where the carburetor precedes the turbo.
Both setups have their unique challenges and benefits. Additionally, ensuring the engine internals can handle the added power is crucial to avoid damaging the engine.
Can You Use A Normal Carb For Turbo?
Using a normal carburetor for a turbocharged engine is possible but not ideal without modifications. Standard carburetors are not designed to handle the pressurized air from a turbocharger. Modifications such as adjusting the fuel jets and float levels, and sometimes adding pressure-resistant parts are necessary.
Specialized carburetors designed for turbocharged applications, known as blow-through carburetors, are often a better choice as they are built to withstand the pressures and provide more consistent fuel metering under boosted conditions.
Can You Supercharge A Carbureted Engine?
Supercharging a carbureted engine is a viable alternative to turbocharging and can be simpler in some aspects. Superchargers provide a more immediate power boost since they are mechanically driven by the engine and don’t suffer from turbo lag.
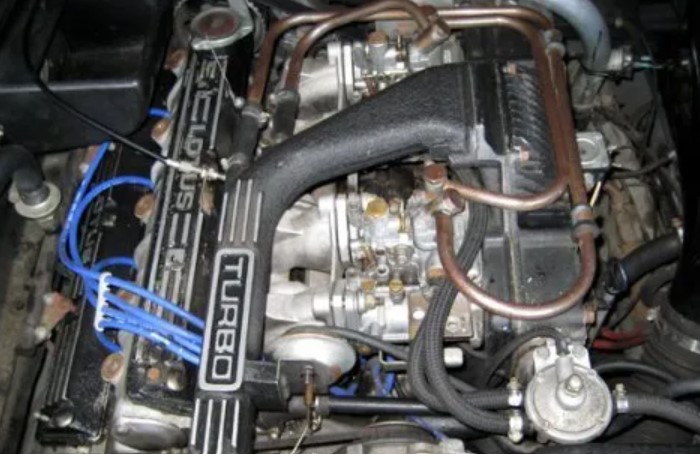

However, similar to turbocharging, the carburetor needs to be modified or replaced with a model designed for forced induction.
Other considerations include ensuring the engine can handle the increased power and possibly upgrading the fuel delivery and ignition systems. Supercharging, while more straightforward in some respects, still requires careful planning and tuning.
Conclusion
Turbocharging a carbureted engine is a transformative process that combines the charm of classic engines with the thrill of modern performance.
By understanding the basics, selecting the right components, and carrying out meticulous installation and tuning, you can significantly enhance your engine’s power and efficiency.
Remember, regular maintenance is key to enjoying the benefits of your turbocharged engine for years to come. Embrace this blend of old and new, and experience the exhilaration of turbocharged power in a carbureted engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Regular Maintenance Does a Turbocharged Engine Require?
Regular maintenance should include checking the turbocharger for leaks or damage, ensuring all connections are secure, monitoring the engine’s oil level and quality, and periodically inspecting and adjusting the carburetor settings.
How Do I Tune My Turbocharged Carbureted Engine?
Tuning involves adjusting the carburetor for the correct air-fuel mixture, setting the ignition timing, and configuring the boost level. This often requires specialized tools and knowledge.
Can I Install a Turbocharger Myself?
While it’s possible for those with mechanical expertise, turbocharging involves complex modifications. It’s usually recommended to seek professional help, especially for tuning and ensuring safe operation.
Is Turbo Lag a Big Issue with Carbureted Engines?
Turbo lag can be more pronounced in carbureted engines compared to fuel-injected ones due to the nature of the fuel delivery system. However, choosing the right turbocharger and tuning can help minimize this issue.
How Much Power Gain Can I Expect?
The power gain varies based on the turbocharger, engine condition, and tuning. Generally, a well-tuned turbocharged engine can see significant power gains, often upwards of 30-40% or more.

Matt Rex brings 12 years of specialized automotive expertise, holding a professional degree in Automotive Engineering Technology. As the founder of Turbochaos, he delivers comprehensive diagnostic services, performance optimization, and fleet maintenance solutions, backed by advanced certifications in hybrid/electric systems and ADAS technology. Its innovative methodologies have earned industry recognition while maintaining a 98% customer satisfaction rate.







